Eye Vitality Plus
Featuring AREDS-2 Nutrients and MAQUIBRIGHT FOR TOTAL EYE HEALTH...
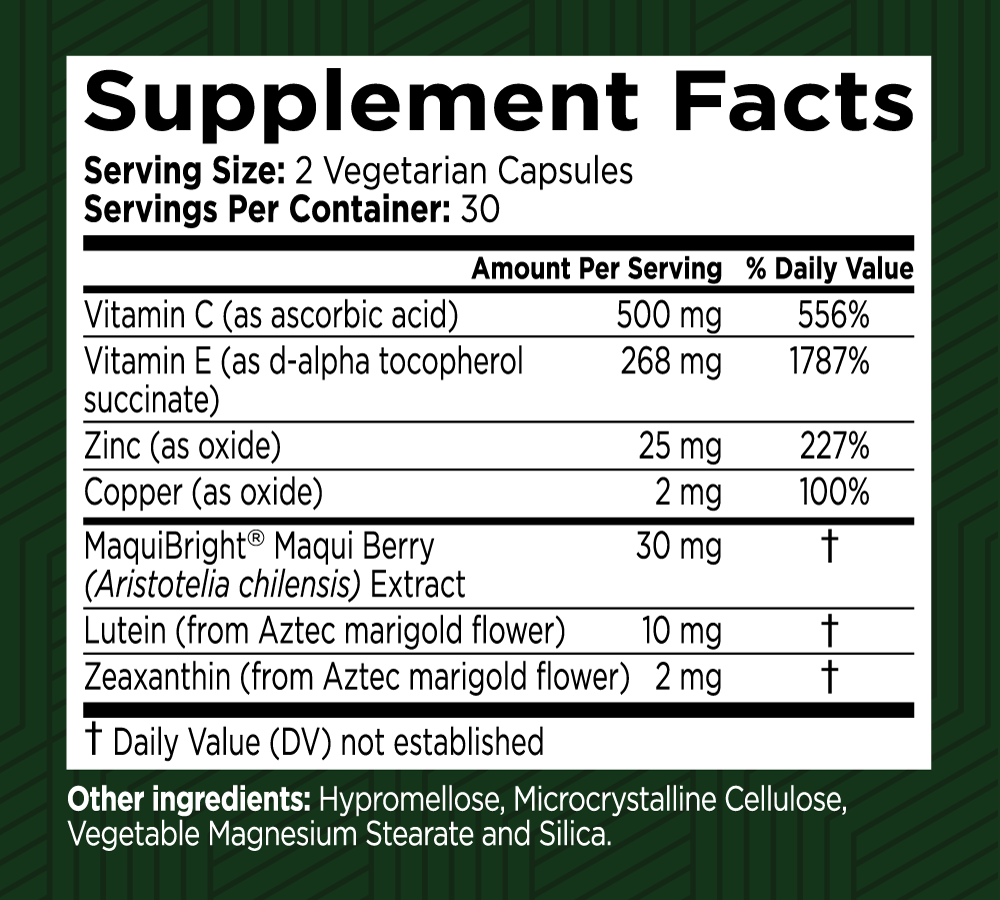
Key Ingredients

MaquiBright® Maqui Berry (Aristotelia chilensis) Extract
Contains the highest concentration of delphinidins, potent antioxidants, among fruits. It helps soothe dry eyes, increases tear production, and combats free radicals.

Lutein (from Aztec marigold flower)
These carotenoids are vital for eye health, particularly for the macula and retina. They protect against UV and blue light, enhance visual acuity, improve glare tolerance, and support overall eye health.

Zeaxanthin (from Aztec marigold flower)
These carotenoids are vital for eye health, particularly for the macula and retina. They protect against UV and blue light, enhance visual acuity, improve glare tolerance, and support overall eye health.

Vitamin C (as Ascorbic Acid)
Vitamin C (as Ascorbic Acid) is a crucial nutrient with a wide range of health benefits. It acts as a powerful antioxidant, supports the immune system, aids in collagen production, and enhances iron absorption. Regular intake of Vitamin C helps protect against oxidative stress, supports cardiovascular and heart health by helping maintain healthy blood vessels and blood pressure, and contributes to the maintenance of healthy skin, bones, and connective tissues. Its role in preventing and reducing the severity of various health conditions makes it an essential component of a balanced, heart-smart diet.

Vitamin E (as d-alpha tocopherol succinate)
Vitamin E (as d-alpha tocopherol succinate) is an essential supplement for protecting cells from oxidative damage. Its potent antioxidant properties support skin health, cardiovascular function, immune response, and overall well-being. Including Vitamin E in your daily regimen can help maintain optimal health and protect against various age-related conditions.

Zinc (as oxide)
Zinc (as Oxide) is a vital supplement that provides essential zinc to support overall health. Its benefits include enhanced immune function, improved skin health, and support for cognitive and reproductive health. Adding zinc to your daily routine ensures that your body receives the necessary nutrients to maintain optimal health and well-being.

Copper (as oxide)
Copper (as Oxide) is an essential supplement that provides a vital source of copper to support overall health. Its benefits include improved cardiovascular health, enhanced immune function, and support for healthy skin and hair. Adding copper to your daily routine ensures that your body receives the necessary nutrients to maintain optimal health and well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
Your health is our top priority
Here at Green Valley, we only work with US-based manufacturing facilities that are cGMP (Good Manufacturing Practices) compliant and FDA inspected.
Our products are triple tested by our manufacturers to ensure potency and purity and are stored in our temperature and humidity-controlled warehouse right here in the Shenandoah Valley, Virginia. And we ship directly to your doorstep – we don’t share warehouse space and we don’t hand off your business to a third party to fulfill your order.
Best of all, all Green Valley products come with our 90-day Satisfaction Guarantee. If you are unhappy with the product for any reason, simply call or email our customer support team and return the unused portion of the product within 90 days of your order. We’ll refund every penny of your purchase (less shipping), no questions asked!

Eye Vitality Plus Customer Reviews
I have been taking Eye Vitality Plus for a few months
I have been taking Eye Vitality Plus for a few months. My night vision is better than it was. I am able to move around in my house in the dark and don't worry about bumping into something. I can move around in my house at night in the dark confidently. I noticed improvement after I had been taking Eye Vitality Plus for a couple of weeks.
I noticed right away that reading small print became easy for me
I noticed right away that reading small print became easy for me. My evening hour for reading became my favorite activity. It actually works.I have been taking Eye Vitality Plus daily since I received it.
I really like the Green Valley Eye Support
I really like the Green Valley Eye Support. I take a variety of eye support supplements. This seems to help my near vision.